Dataviz Code Session: Distribuições
Contents
11. Dataviz Code Session: Distribuições#
11.1. Objetivos da DCS#
Aplicar técnicas de dataviz para plotagem e manipulação de representações visuais de distribuições.
Elaborar RVs para dados de censo (Fonte: UCI ML Repository)
CSV disponível no kaggle.
11.2. Ferramentas utilizadas#
Módulos Python
pandasmatplotlibseaborn
11.3. Aplicação do modelo referencial#
Vide Capítulo 3.
import pandas as pd
import seaborn as sb
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
plt.style.use('../etc/gcpeixoto-datavis.mplstyle') # style sheet
11.3.1. Dados de entrada pré-processados#
Carregamento de dados
df = pd.read_csv('../data/adults.csv',skiprows=1)
df
| age | type-employer | fnlwgt | education | education_num | marital | occupation | relationship | race | sex | capital_gain | capital_loss | hr_per_week | country | income | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0 | 39 | State-gov | 77516 | Bachelors | 13 | Never-married | Adm-clerical | Not-in-family | White | Male | 2174 | 0 | 40 | United-States | <=50K |
| 1 | 50 | Self-emp-not-inc | 83311 | Bachelors | 13 | Married-civ-spouse | Exec-managerial | Husband | White | Male | 0 | 0 | 13 | United-States | <=50K |
| 2 | 38 | Private | 215646 | HS-grad | 9 | Divorced | Handlers-cleaners | Not-in-family | White | Male | 0 | 0 | 40 | United-States | <=50K |
| 3 | 53 | Private | 234721 | 11th | 7 | Married-civ-spouse | Handlers-cleaners | Husband | Black | Male | 0 | 0 | 40 | United-States | <=50K |
| 4 | 28 | Private | 338409 | Bachelors | 13 | Married-civ-spouse | Prof-specialty | Wife | Black | Female | 0 | 0 | 40 | Cuba | <=50K |
| ... | ... | ... | ... | ... | ... | ... | ... | ... | ... | ... | ... | ... | ... | ... | ... |
| 32556 | 27 | Private | 257302 | Assoc-acdm | 12 | Married-civ-spouse | Tech-support | Wife | White | Female | 0 | 0 | 38 | United-States | <=50K |
| 32557 | 40 | Private | 154374 | HS-grad | 9 | Married-civ-spouse | Machine-op-inspct | Husband | White | Male | 0 | 0 | 40 | United-States | >50K |
| 32558 | 58 | Private | 151910 | HS-grad | 9 | Widowed | Adm-clerical | Unmarried | White | Female | 0 | 0 | 40 | United-States | <=50K |
| 32559 | 22 | Private | 201490 | HS-grad | 9 | Never-married | Adm-clerical | Own-child | White | Male | 0 | 0 | 20 | United-States | <=50K |
| 32560 | 52 | Self-emp-inc | 287927 | HS-grad | 9 | Married-civ-spouse | Exec-managerial | Wife | White | Female | 15024 | 0 | 40 | United-States | >50K |
32561 rows × 15 columns
11.4. Visualização de distribuições univariadas#
Podemos usar
seaborn.displotpara plotagens gerais de distribuições:kind=hist | kde | ecdfplotará histograma, ou kernel density estimation, ou ECDFrowecolexpandem plotsA inclusão de
yehuegerará RVs similares a mapas de calor ou, proporções, quando hue for categórico.
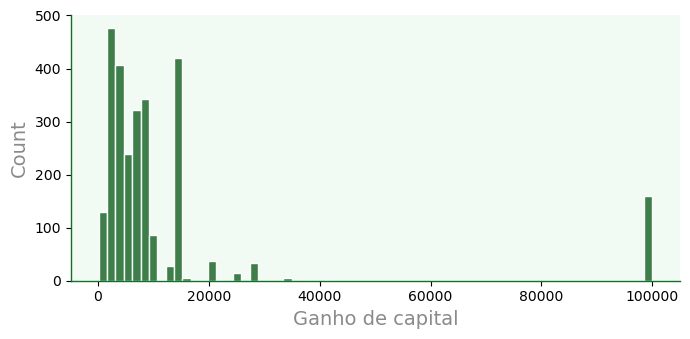
dfa = df[df['capital_gain'] > 0]
# f é figure level
f = sb.displot(data=dfa,
x='capital_gain',
color='#005610',
edgecolor='w',
linewidth=1,
kind='hist', # hist | kde | ecdf
#row='race', # faz outros plots por linha
#col='sex', # faz outros plots por colu
#stat='density', # count | frequency | density | probability | percent | proportion
height=3.5, aspect=2 # aspecto usa proporção de altura
)
# remover grid
for ax in f.axes.flat:
ax.grid(False)
ax.set_xlabel('Ganho de capital')
11.4.1. KDE e superposição#
Com
kdeplot, temos a curva estimada por núcleos, a qual pode ser superposta ao histograma por meio deax.
f2 = sb.kdeplot(data=dfa,
x='capital_gain',
color='#232a00',
fill=False,
alpha=0.9,
ax=f.ax # habilite para sobrepor
)
f2.grid(False)
f2.set_xlabel('Ganho de capital');
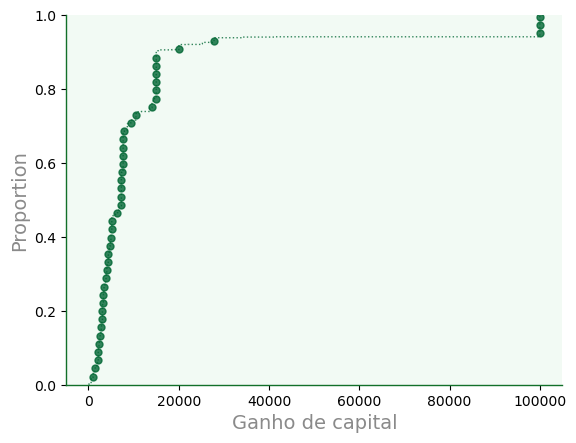
11.4.2. Distribuição cumulativa#
Distribuições cumulativas empíricas podem ser plotadas com
ecdfplot.
f2a = sb.ecdfplot(data=dfa,
x='capital_gain',
color='#006633',
alpha=0.8,
linewidth=1.0,
ls=':',
marker='o',
markersize=5,
markevery=60
#ax=f.ax # habilite para sobrepor
)
f2a.grid(False)
f2a.set_xlabel('Ganho de capital');
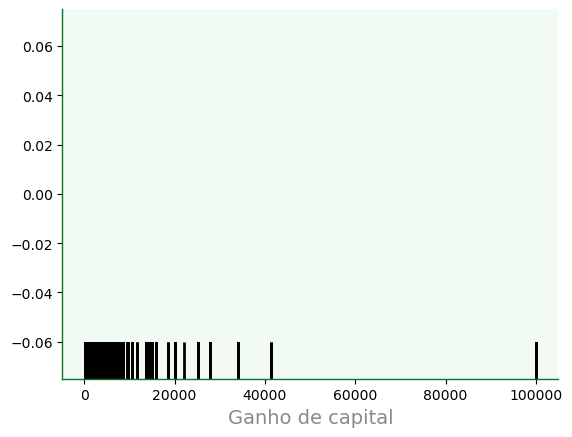
11.4.3. Plot tapete (ou borla)#
O
rugploté uma representação visual que adiciona traços similares a ticks no gráfico. O nome “rug” (tapete) deriva da lembrança de um tapete aberto com suas borlas (franjas) destacadas.Também podemos construir rugs com a keyword
rugemdisplot.
f3 = sb.rugplot(data=dfa,
x='capital_gain',
color='k',
linewidth=2,
height= 0.1,
)
f3.grid(False)
f3.set_xlabel('Ganho de capital');
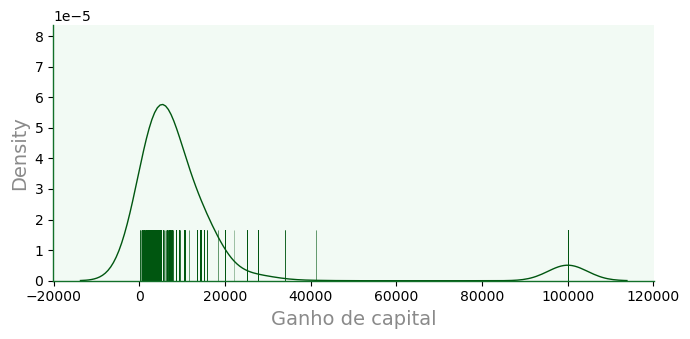
11.4.3.1. Superposição de borlas#
f4 = sb.displot(data=dfa,
x='capital_gain',
color='#005610',
linewidth=1,
kind='kde',
height=3.5,
aspect=2,
rug=True,
rug_kws={
'height': 0.2,
'color': 'w',
'linewidth': 0.5,
'alpha': 0.5,
}
)
for ax in f4.axes.flat:
ax.grid(False)
ax.set_xlabel('Ganho de capital')
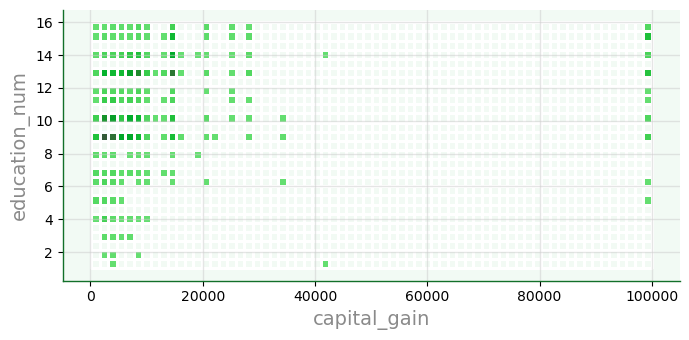
11.4.4. Outros visuais#
Mapa com displot
f5 = sb.displot(data=dfa,
x='capital_gain',
y='education_num',
color='#005610',
edgecolor='w',
linewidth=1,
height=3.5, aspect=2 # aspecto usa proporção de altura
)
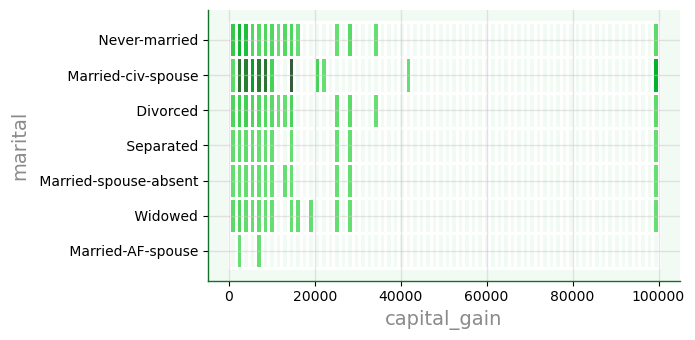
f6 = sb.displot(data=dfa,
x='capital_gain',
y='marital',
color='#005610',
edgecolor='w',
linewidth=1,
height=3.5, aspect=2 # aspecto usa proporção de altura
)
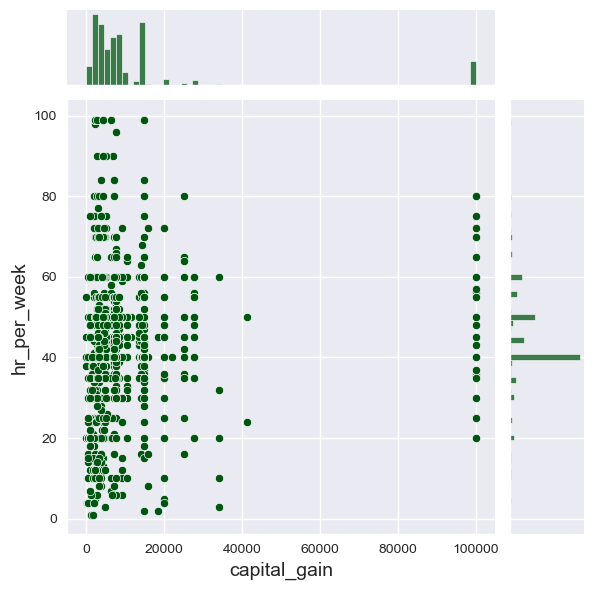
11.5. Distribuições bivariadas#
Usamos
jointplotpara exibir densidades a partir de relações entre duas variáveis.Controle o tipo com
kinde ohue
sb.set_style('darkgrid')
f7 = sb.jointplot(data=dfa,
x='capital_gain',
y='hr_per_week',
color='#005610',
height=6,
#hue='sex'
kind='scatter' # 'scatter', 'hist', 'hex', 'kde', 'reg', 'resid']
)
sb.set_style('darkgrid')
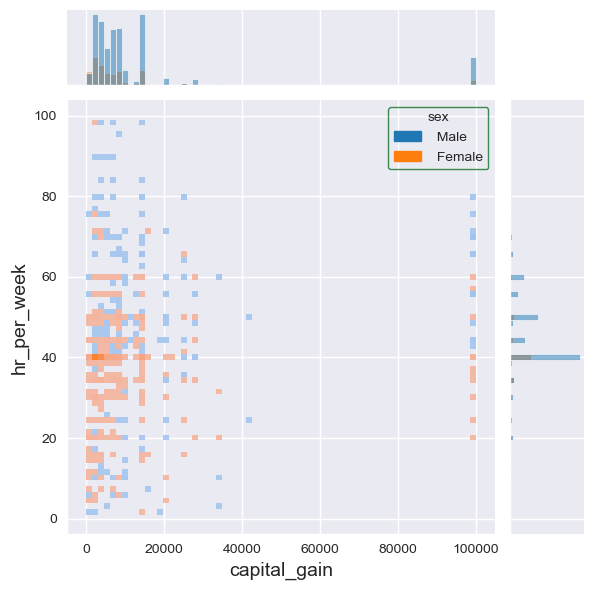
f7a = sb.jointplot(data=dfa,
x='capital_gain',
y='hr_per_week',
color='#005610',
height=6,
hue='sex',
kind='hist' # 'scatter', 'hist', 'hex', 'kde', 'reg', 'resid']
)
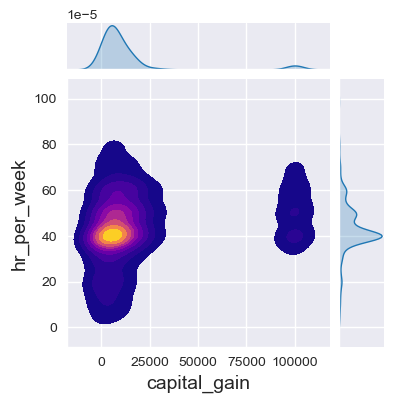
f7c = sb.jointplot(data=dfa,
x='capital_gain',
y='hr_per_week',
height=4,
kind='kde', # 'scatter', 'hist', 'hex', 'kde', 'reg', 'resid'],
fill=True,
cmap='plasma'
)
Usamos
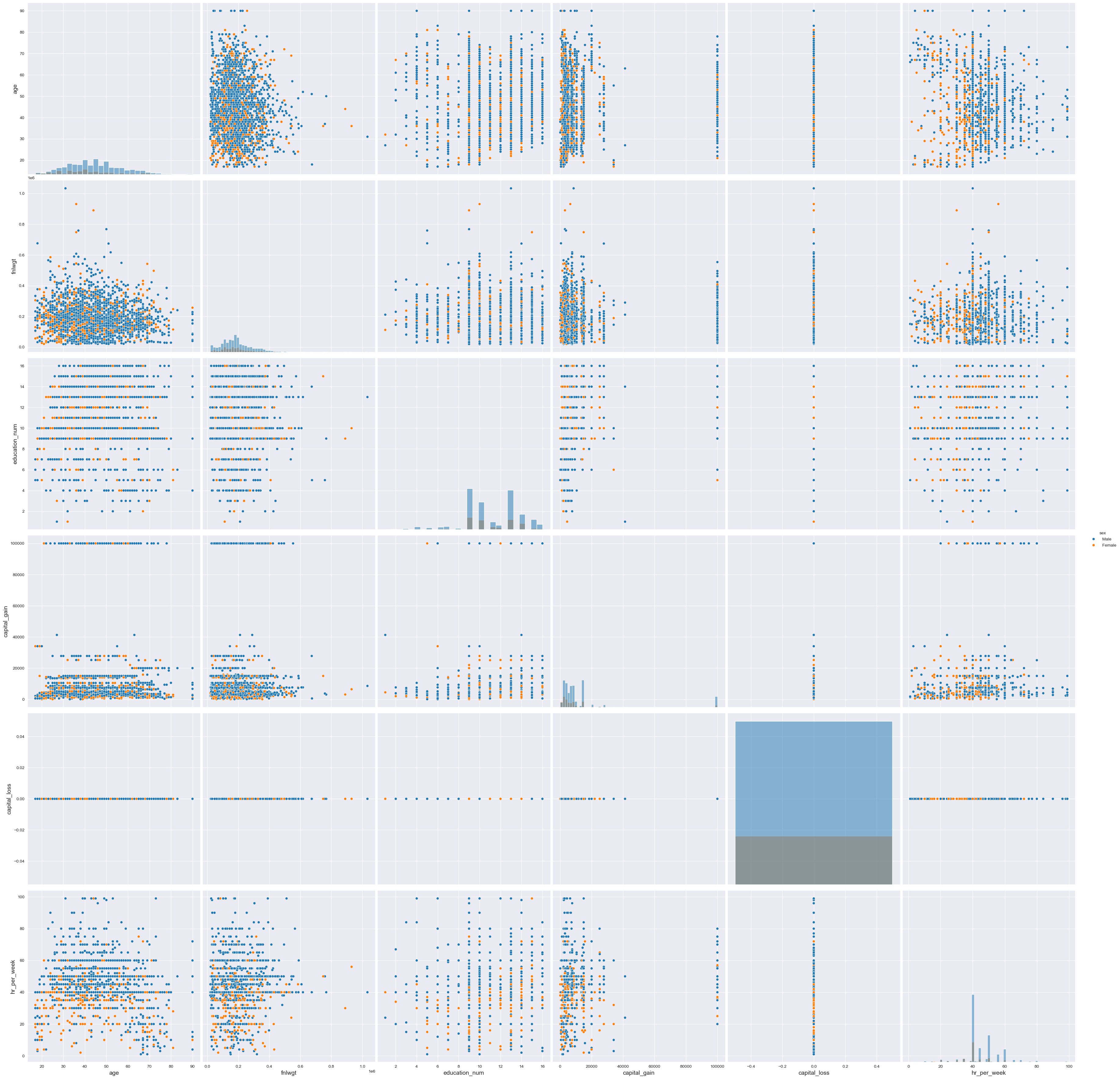
pairplotpara realizar plotagens de pareamentos em forma matricial
f7d = sb.pairplot(data=dfa,
height=6,
hue='sex',
kind='scatter', # 'scatter', 'hist', 'hex', 'kde', 'reg', 'resid'],
diag_kind='hist'
)